NutraCulture™ Englina™
NutraCulture™ Englina™ is a natural dietary supplement and a premium nutritional food, which is the outcome of years of Research of Hash Biotech Labs, India. NutraCulture™ Englina™ is having a unique combination of Phycocyanin enriched Spirulina, Panax ginseng extract with high concentration of ginsenosides and Embilica officinalis (amla) extract. Together they provide us NUTRITION, ENERGY and STAMINA.
NutraCulture™ Englina™ is a vegetarian source of Macro and Micronutrients responsible for providing you energy, stamina and full body revitalization. It contains highest amount of vegetarian complete protein, Vitamins especially Vitamin-B12, Vitamin-C etc., Minerals (Iron, Calcium, Potassium), etc., Phytonutrients like Phycocyanin, Phyllembin, β-carotene, Ginsenosides etc. It also provides essential fatty acids (GLA, ALA, Omega-6, Omega-3) and dietary fibres.
What NutraCulture™ Englina™ contains?
Phycocyanin enriched Spirulina
Spirulina, a super nutritional food, is the richest whole food source available in nature. Spirulina is globally known as “food for the future” because of its amazing ability to synthesize high quality concentrated food more efficiently than any other natural food. This tiny aquatic algae offer up to 69% of plant protein, containing all 9 essential amino acids, vitamins, phytonutrients such as β-carotene, rare essential fatty acid GLA and polysaccharides, thus improving stamina, energy and endurance.
Embilica officinalis (Amla) Extract
Embilica officinalis is one of the most widely used herbs in Ayurveda. It is the highest known natural source of Vitamin C, approximately twenty times higher than an orange. Amla contains high amount of Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) and Vitamin C, which have strong antioxidant properties and help to combat free radicals in the body thereby enhancing the immune system and detoxifying the body.
Panax ginseng Extract
Panax ginseng is a medicinal herb whose main active components are Ginsenosides, which are known to show adaptogenic properties, as it helps to improve immune system, reduces stress and provides extra energy to the body. Ginseng enhances mental and physical recovery from fatigue, regulates blood pressure and aids blood circulation. It also enhances overall cognitive functions of the human body.
Key Components:
Consumption of Nutraculture™ Englina™ in your diet
- Enhances energy levels
- Improves mental ability
- Relieves chronic fatigue
- Controls appetite & obesity
- Reduces anxiety and stress
- Provides complete nutrition with high protein value
- Improves cognitive functions and gives sense of wellness
NutraCulture™ Englina™ for Energy & Stamina
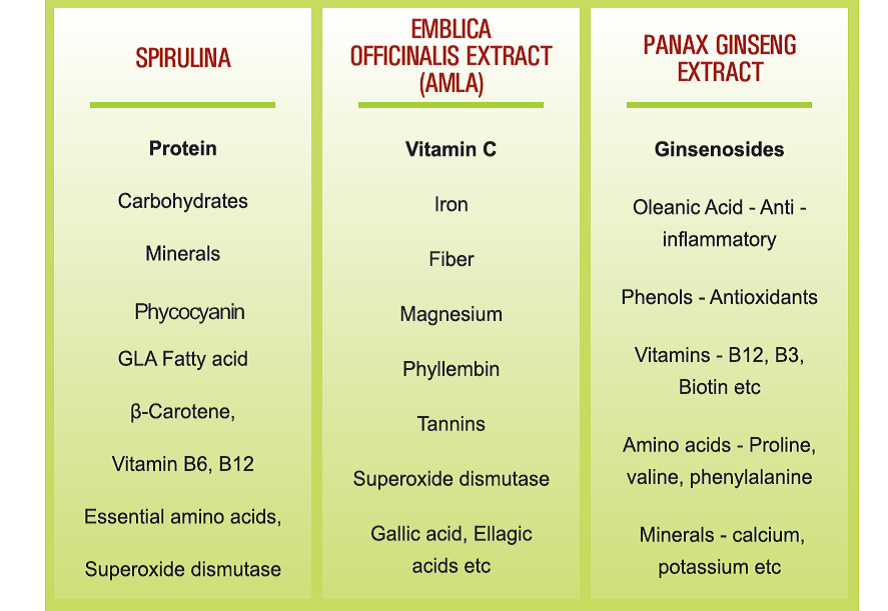
Energy is the ability of body to do work and Stamina is having the strength and energy to endure an activity, illness or stressful situation for an extended period of time. Energy is available in the form of Adenosine-tri-phosphates (ATP), which are also called energy packets of body. ATPs are present in the body in a very small amount and can be used in a matter of seconds. They are produced in our body from proteins, carbohydrates and fats, which are stored in our body tissues. Secondly, vitamins like Niacin, Thiamine, Riboflavin and Minerals like Iron, Zinc, Magnesium play a very important role in the energy production related steps, especially in glycolysis and Kreb`s cycle.
NutraCulture™ Englina™ is a very good source of energy and nutrients like iron, magnesium and trace minerals, which are easy to absorb.
Englina is an attractive supplement especially for athletes as it is helpful for relieving fatigue and improving stamina. Spirulina presence in Englina plays an important role in exercise performance (Kalafati et. al., 2010). Englina enhances protein synthesis due to Emblica in it, which is why it is good for strengthening muscles and building lean muscle mass (Singh et. al., 2010). Ginsenosides in Englina improved oxygen uptake, endurance capacity, vital capacity, forced expiratory volumes and recovery heart rate (Ping et. al., 2011).
As it has its supporting role in normal functioning in case of Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal axis, body`s site for stress hormone, it is suggested to be useful for people with chronic fatigue syndrome (Klatz, 1998). Phycocyanin enriched Spirulina present in NutraCulture™ Englina™ makes it a rich source of natural carotenoid antioxidants that promote cellular health. The anti-fatigue property of P. ginseng is due to its carbohydrate sparing actions during prolonged exercise (Padma and Khosa, 2002). NutraCulture™ Englina™ is helpful in rejuvenation and revitalization of human body due to the availability of Vitamin B12 from Spirulina and P. ginseng which are known for providing the human body with high energy. Further, it contains plant-source glycogen that can be quickly converted by the body for energy. Ginseng present in NutraCulture™ Englina™ has its role in increasing the activity of enzymes involved in glycolysis and kerb cycle, thus increase the production of ATP and hence energy.
References:
- Klatz R. (1998). Ginseng and Memory. The Official Anti-aging Revolution: Stop the Clock Time Is on Your Side, Los Angeles, Nutrition Bytes.
- Padma P, Khosa RL. (2002). Anti-stress agents from natural origin. Journal of Natural Remedies. 2(1): 21-27.
- Kalafati M, Jamurtas AZ, Nikolaidis MG, Paschalis V, Theodorou AA, Sakellariou GK, Koutedakis Y, Kouretas D. (2010). Ergogenic and antioxidant effects of spirulina supplementation in humans. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 42(1):142-51.
- Saini A, Sharma S, Chhibber S. (2008). Protective efficacy of Emblica officinalis against Klebsiella pneumoniae induced pneumonia in mice. Indian J Med Res. 128(2):188-93.
- Ping FWC, Keong CC, Bandyopadhyay A. (2011). Effects of acute supplementation of Panax ginseng on endurance running in a hot & humid environment. Indian J Med Res 133: 96-102.
NutraCulture™ Englina™ for Anti-Aging
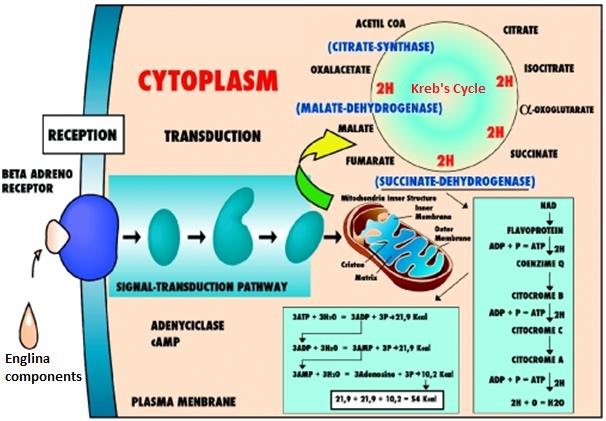
Aging results from the gradual decline in cellular repair and housekeeping mechanisms, which leads to an accumulation of damaged cellular constituents and ultimately to the degeneration of tissues and organs (Gelino and Henson, 2012). It may be due to inbuilt body factors such as damage by free radicals, ischemia, any disease or result of controllable or uncontrollable environmental factors including radiation, nutrition, and lifestyle (drinking, smoking, etc.). In recent years the role played by mitochondria in cellular aging has become the focus of intensive research. Oxidative damage to mitochondrial proteins might cause less efficient processing of oxygen, release of higher levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), free radicals and increased levels of background DNA damage. Since the mitochondria are the site of production of ROS, and so might lead to a significant DNA damage. So for any product to act as anti aging, it must improve the protection of DNA that further guides the protein production.
NutraCulture™ Englina™ is full of antioxidants from all of its three constituents. It contains Phycocyanin, SOD, Vitamin C, E, GSH and Catalases in it. They all help body to scavenge or neutralize free radicals present in body by attenuating oxidative stress in the aging process. Phycocyanin and β-carotene in NutraCulture™ Englina™ from Spirulina have potent antioxidant activity to scavenge free radicals, including alkoxyl, hydroxyl and peroxyl radicals (Deng and Chow, 2010). Ginsenosides from NutraCulture™ Englina™ have an anti-oxidant effect that results in decrease of harmful free radical formation and lipid peroxidation (Kim, 2012). Koreans have traditionally used ginseng roots and root extracts to revitalize the body and mind, increase physical strength, prevent aging, and increase vigor. Vitamin C and other anti-oxidants from NutraCulture™ Englina™ controls lipid metabolism and protein expression involved in oxidative stress during aging, protects the skin from damaging effect of free radicals and transition metals induced oxidative stress (Kuttan and Harikumar, 2012).
References:
- Gelino S, Hansen M. (2012). Autophagy - An Emerging Anti-Aging Mechanism. Journal of Clinical & Experimental Pathology.; 84, 1-12.
- Kim JH. (2012). Cardiovascular Diseases and Panax ginseng: A Review on Molecular Mechanisms and Medical Applications. J. Ginseng Res.; 36 (1), 16-26.
- Deng R, Chow TJ. (2010). Hypolipidemic, Antioxidant, and Antiinflammatory Activities of Microalgae Spirulina. Cardiovascular Therapeutics.; 28(4), e33–e45
- Kuttan R, Harikumar KB. (2012). Phyllanthus Species: Scientific Evaluation and Medicinal Applications, Boca Raton, CRC Press, pp-269.
NutraCulture™ Englina™ for Stress & Anxiety
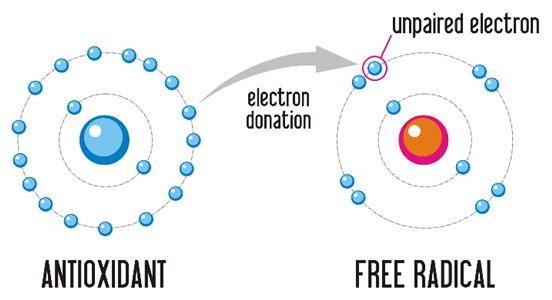
Adaptation to altering physical and social circumstances requires integration of behavioral, neuroendocrine and autonomic responses to maintain homeostasis. Stress is defined as any perturbation of homeostasis. It can be psychological or physiological in nature. The principal components of the stress response consist of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) system (most commonly known as the HPA axis) & Symphatetic nervous system (SNS) or the locus coeruleus-norepinephrine (LC-NE) system (Verbrugghe et. al., 2012).
Adaptogens or antistress agents modulate our response to stress (physical, environmental, or emotional) and help regulate the interconnected endocrine, immune, and nervous systems. This re-regulation of a disordered or highly stressed system is achieved by metabolic regulators such as cytokines, catecholamines, glucocorticoids, cortisol, serotonin, nitric oxide (NO), cholecystokinin, corticotrophin-releasing factor (CRF), and sex hormones (Panossian, 2003).
NutraCulture™ Englina™holds its anti-stress status due to the combined effect of all of its components.
Phycocyanin enriched Spirulina present in NutraCulture™ Englina™ inhibit stress induced activation of HPA axis and sympathetic stimulation and functional alterations of the cell membrane due to steroidal storm. It further prevents adrenal gland hyperactivity, which can become the cause of anxiety. Spirulina presence in NutraCulture™ Englina™ makes it beneficial for lowering our anxiety too. Spirulina also helps to protect the body against free radicals formed due to stress, as it contains anti-oxidants like beta-carotene, superoxide dismutase, selenium and vitamin E.
Ginseng present in NutraCulture™ Englina™ has the ability to directly impact both the adrenal glands and the HPA axis (Kathleen and Gregory, 2009). It suppresses catecholamine synthesis induced under stressful conditions via the reduction of catecholamine, synthesizing enzymes, gene expression and leading to the recovery of homeostasis (Kim et. al., 2010). It modulates hormone release and act as a tonic to the overactive adrenal glands, thus help in relieving anxiety.
E. officinalis present in NutraCulture™ Englina™ imparts its antistress activity, partly due to its tendency to normalize stress-induced perturbations in oxidative free radical scavenging activity (Mehta and Joshi, 2010; Bhattacharya et. al., 2000). Further tannins play an important role as hypo-lipidaemic agent that directly acts upon sympatho-adrenal axis and lowers the synthesis of corticosterone (Sairam et. al., 2003).
References:
- Panossian, A. (2003). Adaptogens, Tonic Herbs for Fatigue and Stress. Alt. Complement Ther. 9(6):327-331.
- Verbrugghe E, Boyen F, Gaastra W, Bekhuis L, Leyman, B, Parys AV, Haesebrouck F, Pasman F. (2012). The complex interplay between stress and bacterial infections in animals. Veterinary Microbiology. 155 (2–4): 115–127.rticle
- Kathleen A, Gregory SK. (2009). Nutrients and Botanicals for Treatment of Stress: Adrenal Fatigue, Neurotransmitter Imbalance, Anxiety, and Restless Sleep. Alternative Medicine Review. 14 (2): 114-140.
- Kim Y, Choi EH, Doo M, Kim JY, Kim CJ, Kim CT, Kim HI. (2010). Anti-stress effects of ginseng via down-regulation of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and dopamine β-hydroxylase (DBH) gene expression in immobilization-stressed rats and PC12 cells. Nutr Res Pract. 4(4):270-275
- Mehta CS, Joshi VR. (2012). Anti ageing drugs in Ayurveda. International Journal of Green and Herbal Chemistry. 1(1): 61-74.
- Bhattacharya A, Ghosal S, Bhattacharya, SK (2000). Antioxidant activity of tannoid principles of Emblica officinalis (amla) in chronic stress induced changes in rat brain. Indian Journal of Experimental Biology. 38(9): 877-880.
- Sairam M, Neetu D, Deepti P, Vandana M, Ilavazhagan G, Kumar D, Selvamurthy W. (2003). Cytoprotective activity of Amla (Emblica officinalis) against chromium induced oxidative injury in murine macrophages. Phytoether. Res. 17: 430-432.
NutraCulture™ Englina™ for Immunity
The immune system is the body's defense against infectious organisms and other invaders through a series of steps called the immune response. The immune system is composed of two major subdivisions named as Innate or Nonspecific immune system and Adaptive or Specific immune system. Both aspects of the immune system have cellular and humoral components by which they carry out their protective functions. In addition, there is interplay between these two systems, i.e., cells or components of the innate immune system influence the adaptive immune system and vice versa.
Organs comprising the immune system are Bone Marrow, Thymus, Spleen, Lymph Nodes. Cells of the immune system are B-cells, T-cells, Natural Killer cells, Macrophages, Dendritic cells.
Cells of the innate immune system include phagocytic cells, NK cells, basophils, mast cells, eosinophiles and platelets. Cells that make up the adaptive immune system include the B and T lymphocytes. A specialized subset of cells called antigen presenting cells (APCs) are a heterogenous population of leukocytes that play an important role in innate immunity and also act as a link to the adaptive immune system by participating in the activation of helper T cells (Th cells). These cells include dendritic cells and macrophages (Male et. al., 2006).
- Immune system needs a lot of the body's resources to function; any decline in essential nutrients is likely to have an effect on it. When there is scarcity of nutrients, the body tends to favour the brain and certain other organs, and this can also affect the immune system.
- Stress is another factor which can affect immune function.
Most nutrients with antioxidant capacity (eg. Vitamin C, E, selenium, beta-carotene and other carotenoids) are associated with enhancing immune function. Thus it is always best to eat a balanced, and healthy, diet.
NutraCulture™ Englina™ works by strengthening the immune system, making the body produce more red and white blood cells and provides protection against microbes, thus enhance the overall immunity of the host. Phagocytes play important roles in our innate immune defence against infectious microbes and in activating the adaptive immune response (Yuandani et. al., 2013). All the three constituents of NutraCulture™ Englina™ increases phagocytic index (Ragap et. al., 2012; Saini et. al., 2008; Lim et. al., 2004) and thus are defensive against microbial infections. Because of the antioxidants presence in NutraCulture™ Englina™, defence mechanism is strengthened against free radical damage, induced during stress (Reg et. al., 1999). Spirulina from NutraCulture™ Englina™ acts directly on myeloid lineages and either directly or indirectly on Lymphocytes, Macrophages, Hematopoetic stem cells and NK cells (Blinkova et. al., 2001; Hirasahi et. al., 2002). It also stimulates the production of Interferon gamma (IFN-γ) and other cytokines (Yakoot et. al., 2012; Hirasahi et. al., 2002). E. officinalis present in Nutraculture Englina increases humoral and cellular immune responses, by either enhancing cytokine secretion, or by directly stimulating B-lymphocytes or T-lymphocytes (Baliga et. al., 2011). They further increase red blood cell count in body and raising Hb levels (Patel et. al., 2009; Anila and Vijayalakshami, 2000). Ginseng present in Nutraculture Englina has immuno-modulating activity by affecting the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. It further enhances natural killer (NK) cell activity and increased immune cell phagocytosis and reduce the risk of viral infections (Krylov AV, et. al., 1972; Nakagawa S, et al., 1985).
References:
- Male D, Brostoff J, Roth DB, Roitt I. (2006). Immunology- Seventh Edition, Canada, Mosby Elsevier.
- Yuandani, Ilangkovan M, Jantan I, Mohamad HF, Husain K, Razak AFA. (2013). Inhibitory Effects of Standardized Extracts of Phyllanthus amarus and Phyllanthus urinaria and Their Marker Compounds on Phagocytic Activity of Human Neutrophils. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2013:1-9.
- Ragap HM, Khalil RH, Mutawie HH. (2012). Immuno-stimulant effects of dietary Spirulina platensis on tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science 02 (02): 26-31.
- Lim TS, Na K, Choi EM, Chung JY, Hwang JK. (2004). Immunomodulating activities of polysaccharides isolated from Panax ginseng. J Med Food. 7(1):1-6.
- Rege NN, Thatte UM, Dahanukar SA. (1999). Adaptogenic properties of six rasayana herbs used in Ayurvedic medicine. Phytother Res. 13(4): 275-91.
- Blinkova LP, Gorobets OB, Baturo AP. (2001). Biological activity of Spirulina. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 2:114-8.
- Baliga MS and Dsouza JJ. (2011). Amla (Emblica officinalis Gaertn), a wonder berry in the treatment and prevention of cancer. European Journal of Cancer Prevention, 20:225–239.
- Yakoot M, Salem A. (2012). Spirulina platensis versus silymarin in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus infection. A pilot randomized, comparative clinical trial. BMC Gastroenterology. 12:32-40.
- Anila L, Vijayalakshmi NR. (2000). Beneficial effects of flavonoids from Sesamum indicum, Emblica officinalis and Momordica charantia. Phytother Res. 14(8): 592-5.
- Krylov AV, Kostin VD, Chuyan AH. (1972). Effect of juices from Araliaceae plants on the infectivity of phytopathogenic viruses. Acta Virol.16 (1):75-76.
- Nakagawa S, Yoshida S, Hirao Y, Kasuga S, Fuwa T. (1985). Cytoprotective Activity of Components of Garlic, Ginseng and Ciuwjia on Hepatocyte Injury Induced by Carbon Tetrachloride in vitro. Hiroshima J Med Sci. 34:303-09.
- Patel, S.S., Shah, R.S. and Goyal, R.K. (2009). Antihyperglycemic, antihyperlipidemic and antioxidant effects of Dihar, a polyherbal ayurvedic formulation in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Ind. J. Exp. Biol. 47: 564-570.
- Hirahashi T, Matsumoto M, Hazeki K, Saeki Y, Ui Mc, Seya T. (2002). Activation of the human innate immune system by Spirulina: Augmentation of interferon production and NK cytotoxicity by oral administration of hot water extract of Spirulina platensis. International Immunopharmacology. 2: 423– 434.
NutraCulture™ Englina™ for Memory & Cognitive Functions
A person’s brain development and cognitive abilities for their entire life are strongly determined by the nutritional status of both child and mother during perinatal period. Micronutrients, proteins and essential fatty acids are essential for proper growth & structure of brain as well as for activity of multiple enzymes required in metabolic and signalling pathways.
Memory is the ability of an individual to record sensory stimuli, events, information, etc., retain them over short or long periods of time and recall the same at a later stage when needed (Rathee et. al., 2008). Memories are stored in network of brain cells and form links between different brain cells, by interconnecting neuronal dendrites. For a memory to be made it must enter the cell by seeing, hearing or doing something, which accounts for the three kinds of memory – visual, auditory or kinesthetic. If a memory involves all three, it will exist in a maximum number of brain cells.
Memory loss is caused by damage to neurons & neuro-transmitter pathway involved in encoding, storing & retrieving memories. Any factor that reduces the amount of Acetylcholine (ACh) will put negative effects on memory.
Memory enhancers are nutraceuticals that are supposed to improve mental functions such as cognition, memory, intelligence, motivation, attention and concentration by increasing the level of neurotransmitters, particularly acetylcholine (ACh), and improve blood flow to the brain, thereby increasing its oxygen and nutrient supply, which will aid brain function and memory. Substances such as flavonoids, and tannins that possess memory improving activity are of particular therapeutic importance (Shiksharthi et. al., 2011). The natural memory enhancing drugs control the activity of acetyl-cholinesterase (AChE). AChE modulates ACh to proper levels by degradation. Accordingly excessive AChE activity results in ACh deficiency which leads to memory and cognitive impairements. These natural agents inhibit the excessive AChE activity and protect the people suffering with dementia (Shiksharthi et. al., 2011).
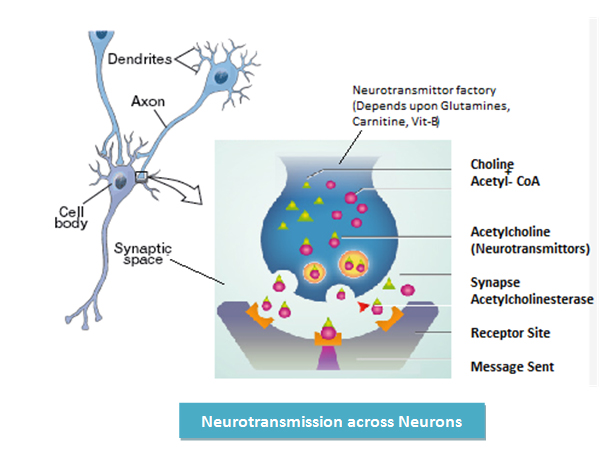
Ginseng from NutraCulture™ Englina™ increase neuronal activity and ACh activity in brain. Emblica from NutraCulture™ Englina™ inhibits cholinesterase (Vasudevan and Parle 2007; Reddy et. al. 2010). Vitamin B complex (B6, B9, B12) and folate present in NutraCulture™ Englina™ from Spirulina improve oxygen and nutrient transport to brain cell by RBC production and also contribute to age-associated cognitive impairment (Ingole et. al., 2008). Antioxidants present in NutraCulture™ Englina™ from all of its three constituents decrease oxidative stress in CNS by mopping up harmful free radicals & ROS that may damage nerves thus preserve neural network. They constantly scavenge CNS for damaged neurons and harmful agents (Hwang et. al., 2011; Pabon et. al., 2012).
References:
- Rathee P, Chaudhary H, Rathee S, Rathee D. (2008). Natural memory boosters, Pharmacognosy Review.; 2(4): 249-256.
- Shiksharthi AR, S and Ramana J. (2011). Systematic Review of Herbals as Potential Memory Enhancers, International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Sciences.; 2(3): 918-925.
- Ingole SR, Rajput SK and Sharma SS. (2008). Cognition Enhancers: Current Strategies and Future Perspectives. CRIPS; 9(3): 42-48.
- Vasudevan M, Parle M. (2007). Effect of Anwala churna (Emblica officinalis Gaertn.): An ayurvedic preparation on memory deficit rats. Yakugaku Zasshi.; 127(10):1701-7.
- Reddy KY, Lakshmi SM, Kumar AS. (2010). Review on effect of Natural memory enhancing drugs on dementia. International Journal of Phytopharmacology.; 1(1): 1-7.
- Pabon MM, Jernberg JN, Morganti J, Contreras J, Hudson CE, Klein RL, Bickford PC. (2012). A Spirulina-enhanced diet provides neuroprotection in an α-synuclein model of Parkinson’s disease. PLoS One.; 7(9).
- Hwang JH, Lee IT, Jeng KC, Wang MF, Hou RC, Wu SM, Chan YC. (2011). Spirulina prevents memory dysfunction, reduces oxidative stress damage and augments antioxidant activity in senescence-accelerated mice. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo).; 57(2):186-91.
NutraCulture™ Englina™ for High Blood Pressure & Cardiac Health
Hypertension or high blood pressure is a medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is elevated, due to which heart has to work harder than normal to circulate blood through the vessels. Cardiovascular disease is a class of diseases that involve the heart and blood vessels. The causes of cardiovascular disease are diverse but Athersclerosis and Hypertension are the most common.
E. officinalis present in NutraCulture™ Englina™ helps in reducing oxidative stress, prevents development and progression of hypertension as well as cardiac and renal hypertrophy. It also helps in increasing the serum NO, K+ levels and decreased Na+ levels (Bhatia et. al., 2011). Further, Phyllembin (ethyl gallate), an active component introduced in NutraCulture™ Englina™ from E. officinalis may act on cardiovascular and other system by increasing the action of adrenalin (Tariq et. al., 1977). It produces coronary dilation and peripheral vasoconstriction which control the amount of blood flow through heart and skin. Ginseng provides cardiovascular and hypertension benefits to NutraCulture™ Englina™ through diverse mechanisms that include antioxidation, modifying vasomotor function, reducing platelet adhesion, influencing ion channels, altering autonomic neurotransmitters release, and improving lipid profiles (Kim 2012).
References:
- Bhatia J, Tabassum F, Sharma AK, Bharti S, Golechha M, Joshi S, Sayeed Akhatar M, Srivastava AK, Arya DS. (2011). Emblica officinalis exerts antihypertensive effect in a rat model of DOCA-salt-induced hypertension: role of eNOS, NO and oxidative stress. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 11(3): 272-9.
- Tariq M, Hussain SJ, Asif M, Jahan M. Protective effect of fruit extracts of Emblica officinalis (Gaertn.) & Terminalia bellerica (Roxb.) in experimental myocardial necrosis in rats. Ind J Exp. Biol. 1977; 15: 485-486.
- Kim JH. (2012). Cardiovascular Diseases and Panax ginseng: A Review on Molecular Mechanisms and Medical Applications. J. Ginseng Res. 36 (1): 16-26.
NutraCulture™ Englina™ for Diabetes
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder due to Insufficient production of Insulin, Production of defective Insulin or Inability of cells to use insulin properly and efficiently.
Insulin is a peptide hormone produced by β cells of Pancreas. It aids in entrance of glucose in cells and regulation of glucose level in blood.
Englina has significant positive effect on people suffering from type 2 diabetes. It provides glycogen, capable of rapidly generating energy for the body without causing additional burden on pancreas and result in low blood glucose level.
Phycocyanin enriched Nutraculture Spirulina present in NutraCulture™ Englina™ stimulate glycogenesis in the liver and helps in utilization of glucose at peripheral sites (Fayzunnessa et. al., 2011). It also inhibits endogenous synthesis of lipids & down regulation of lipogenesis, thus enhance high resistance for diabetes (Layam and Reddy et. al., 2007). Emblica officinalis presence in NutraCulture™ Englina™ enhance basal insulin output, potentiates glucose stimulated insulin secretion and inhibit protein glycation and starch digestion (Kasabari et. al., 2010). Ginseng in NutraCulture™ Englina™ from Panax ginseng targets modulation of insulin production from pancreatic β-cells and glucose metabolism by target tissues (Yuan et. al., 2012).
References:
- Fayzunnessa N, Morshed NA, Uddin A, Parvin A, Saifur R. (2011). In vivo study on the efficacy of hypoglycemic activity of Spirulina plantesis in long evan rats. International Journal of Biomolecules and Biomedicine. 1(1): 27-33.
- Layam A, Reddy CLK. (2007). Antidiabetic property Of Spirulina. Diabetologia Croatica.35 (2): 29-33.
- Yuan HD, Kim JT, Kim SH, Chung SH. (2012). Ginseng and Diabetes: The Evidences from In Vitro, Animal and Human Studies. J Ginseng Res. 36(1): 27–39.
- Kasabri V, Flatt P, AbdelWahab Y. (2010). Emblica officinalis stimulates the secretion and action of insulin and inhibits starch digestion and protein glycation. Endocrine Abstracts. 22: P293.
Who Should Consume NutraCulture™ Englina?
NutraCulture™ Englina™ is a unique herbal formulation. It is widely recommended for:
- Athletes and sportspersons.
- People afflicted by fatigue.
- Those having a heavy work load.
- Strengthening the immune system.
- Those who are health conscious.
- Those who want to improve their stamina.
- Those lacking optimum energy levels.
- Those who feel sleepy and cannot concentrate.
- Those who are involved in tough physical and mental activities.
Directions
- NutraCulture™ Englina™ can be taken after the meals any time during the day, preferably after breakfast.
- NutraCulture™ Englina™ can be taken by everybody over 12 years of age and is also suitable for diabetics.
Recommended Dosage:
- The intake should be 3-4 tablets per day.
- NutraCulture™ Englina™ is completely safe and can be consumed daily.
- A regular course of NutraCulture™ Englina™ takes care of your daily nutritional requirement, energy level and keeps your body healthy.
Advisory:
Consult your family physician before taking any food or dietary supplement
