Nutraculture™ Spirulina
- Spirulina for Nutrition
- Spirulina for Anemia
- Spirulina for Immunity
- Spirulina for Diabetes
- Spirulina for High BP
- Spirulina for Cholesterol
- Spirulina for Anti-Aging
- Spirulina for Allergy
- Spirulina for Anti Cancer
- Spirulina for Weight Management
- Spirulina for Beauty
- Spirulina for Thyroid
- Spirulina for Fertility
- Spirulina for Pregnant and Nursing Mothers
Phycocyanin enriched Nutraculture™ Spirulina:
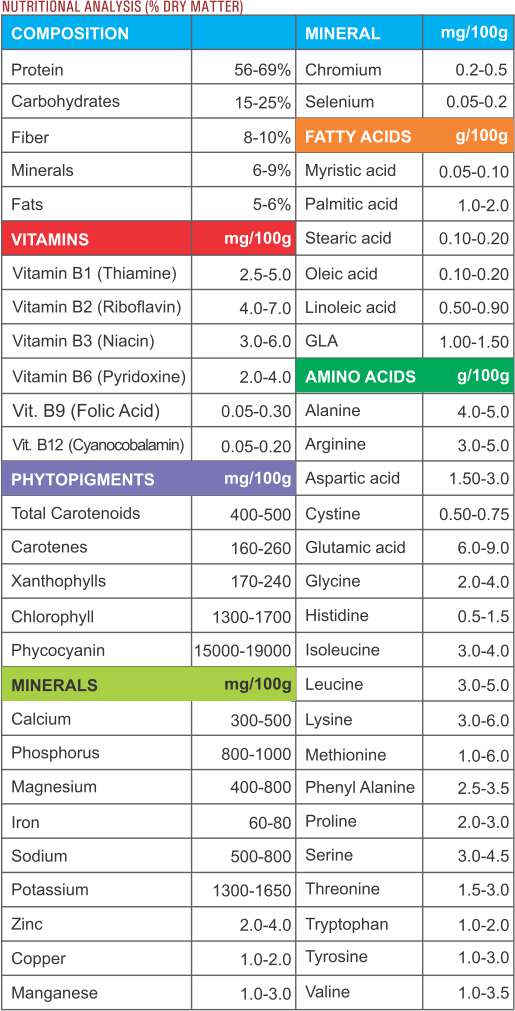
Spirulina is the new dawn for a healthy and active mind and body. It increases absorption of nutrients and helps protect against infections by enhancing immune system. It is immensely beneficial to humans with high nutrient content including complete proteins with customised absorbability, all essential amino acids in right proportion, vitamins, minerals, antioxidants and phytonutrients required for rejuvenation of cells. Further, presence of essential fatty acids such as GLA is good for heart and combating stress.
Facts about Phycocyanin enriched Nutraculture™ Spirulina:
A person cannot overdose on Spirulina.
- It is a whole food, not a concentrate, not an extract.
- It is 100% Natural, 100% vegetarian.
- Spirulina is the richest source of natural antioxidants.
- It contains 18 amino acids including all the 9 essential amino acids, in optimum ratio which required by our body for proper working and development.
- Spirulina help prevent cancers and viral diseases in human.
- Spirulina has 58 times more iron than raw spinach.
- Spirulina contains the highest amount of vegetarian protein, which is water soluble, easily digestible and simply discharged by your system as water and not stored as fat.
Spirulina platensis, a blue - green algae, is the richest whole-food source available in nature and it gets its name from the shape of the plant which looks like little spirals. The dark green colour of Spirulina comes from the high amount of chlorophyll, plant blood, which is only one molecule different to haemoglobin in human blood.
Phycocyanin enriched Nutraculture™ Spirulina for Nutrition:
Proper nutrition can help prevent disease and promote health. No one fruit, vegetable or meat can provide everything the human body demands, but the tiny Spirulina comes so close to this ideal. Spirulina more importantly provide the wide range of essential vitamins, minerals and protein which the human body uses as fuel and catalyst.
COMPLETE PROTEINS
Nutritional qualities of Spirulina are truly one-of-a-kind. It is highest natural source of protein (up to 70%) ever discovered. Proteins present in Spirulina are biologically complete, which means they provide all nine essential amino acids in the proper ratios. Furthermore, Spirulina provides all the required amino acids in a form, which is easier to digest than animal or soy protein.
Functions of Essential Amino acids:
- Isoleucine: It is used for energy by muscle tissue.
- Leucine: Leucine helps in increasing cognitive functions of brain and reduces muscle protein breakdown.
- Lysine: It helps form collagen, aids in the production of antibodies, hormones and sufficient absorption of calcium.
- Methionine: It prevents disorders of the hair, skin and nails, lowers blood cholesterol levels, reduces liver fat and protects the kidneys.
- Phenylalanine: It stimulates metabolic rate and required by the thyroid gland, helps in producing norepinephrine.
- Threonine: It prevents fat build-up in the liver, assists digestion & metabolism.
- Tryptophan: It acts as natural relaxant, thus helps in treatment of migraine headaches, works with lysine in reducing cholesterol levels.
- Valine: It promotes mental vigor, muscle coordination and calm emotions.
- Histidine: It restores tissues and sustaining the myelin sheaths which shield the nerve cells. Helpful in the production of the red and white blood cells and protection from eczema.
Functions of Non- Essential Amino acids
- Alanine: It strengthens cellular walls.
- Arginine: It is important to male sexual health as seminal fluid is 80 percent arginine. It also helps in detoxificationy the blood.
- Aspartic acid: It aids transformation of carbohydrates into cellular energy.
- Cystine: It aids pancreatic health, which stabilizes blood sugar and carbohydrate metabolism. It has been used to alleviate some symptoms of food allergy and intolerance.
- Glutamic acid: It is one of the principal fuels for the brain cells with glucose. It has been used to reduce the craving for alcohol and stabilize mental health.
- Glycine: It promotes use of energy and oxygen in the cells.
- Proline: It is a precursor of glutamic acid.
- Serine: It helps form the protective fatty sheaths surrounding nerve fibers.
- Tyrosine: It slows down aging of cells and suppresses hunger centers in the hypothalamus. It can be synthesized from phenylalanine and involved in proper coloration of hair and skin, including protection from sunburn.
Digestibility and Availability of Spirulina Proteins:
When most people think of protein, products such as meat, eggs, and fish come to mind. Many of us don’t realize that we can get protein from vegetarian source as well. Spirulina contains upto 70% vegetable protein, which is much higher than fish, pork, or beef. Animal protein is a much bigger molecule than vegetable protein, and is much harder for our system to digest. When too much animal protein is eaten, it is deposited in our body as fat. Too much fat will cause high cholesterol levels and may impact our heart and blood vessels. Digestibility of protein is 83-90% in ordinary dried Spirulina (Dillon and Phan, 1993).
Comparison of Spirulina protein and other foods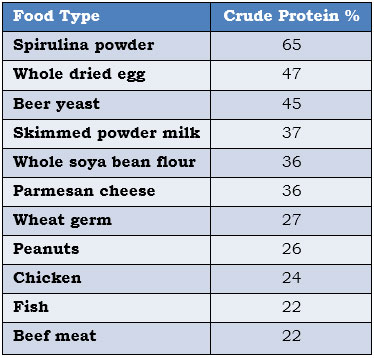
Reference:
- Dillon JC, Phan PA. (1993). Spirulina as a source of proteins in human nutrition, Bull. Inst. Océano, Monaco, Special 12: 103-107.
CARBOHYDRATES
Spirulina contains only 15 to 25% carbohydrates. The primary forms of carbohydrates are rhamnose and glycogen, two polysaccharides which are easily absorbed by the body with minimum insulin intervention. Spirulina is the only known vegan source of glycogen. Spirulina offers quick energy, without taxing the pancreas or precipitating hypoglycemia.
ESSENTIAL FATTY ACIDS
Humans require a dietary source of essential fatty acids (EFA). They promote cholesterol normalization and are precursors for hormones, called prostaglandins. Spirulina has 4 to 7% lipids, or fats, and most of these are essential fatty acids.
GLA is the precursor to the body’s prostaglandins – master hormones that control many functions. Dietary saturated fats and alcohol can cause in GLA deficiency and suppressed prostaglandin formation. Studies show GLA deficiency figures in many diseases and health problems,so a food source of GLA can be important. The only other known sources of dietary GLA are mother’s milk and oil extracts of evening primrose, black currant and borage seeds.
MINERALS
Although proteins are the building blocks of life, many trace minerals can profoundly affect health and metabolism. Spirulina contains essential minerals and trace elements absorbed from its growth medium into chelated, easily absorbed forms:
- Potassium: It is a crucial mineral that regulates body electrolyte balance. Deficiency can cause heart arrest, hypertension, adrenal exhaustion and muscular collapse.
- Zinc: Zinc is an important component of over 200 metalloenzymes and there is high concentration of zinc in the brain. Required for mental growth, optimal functioning of endogenous antioxidants like glutathione peroxidase, superoxide dismutase, catalases and ceruloplasmin. Deficiency of Zinc can lead to Lethargy, decreased visual memory, impaired cognitive development and neuropsycho-logical problems.
- Calcium: It is one of the most abundant mineral in the body and important to bone and dental health, but is also involved in neural transmissions to the muscles.
- Magnesium: Deficiency of magnesium can lead to spasmodic muscle disorders, including cardiac irregularities. It helps assimilation of vitamin C, B vitamins and protein.
- Manganese: It activates enzyme systems, along with zinc. It promotes activity of neurotransmitter acetylcholine, and helps stabilize blood sugar.
- Selenium: Originally it was supposed to be a toxic heavy metal, but now known to be necessary for health. It retards aging, harmful oxidation and free radical formation, reduces the toxic effect of carcinogens, and improves cardiac efficiency.
- Iron: It promotes formation of hemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying blood pigment found in healthy red blood cells. Iron deficiency is most common among women in their reproductive years.
- Phosphorus: The second most abundant mineral in the human body, it is found in practically every cell. Functions with calcium to maintain bone density. Helps to digest carbohydrates and the B vitamins i.e. niacin and riboflavin.
- Sodium: Sodium helps control blood pressure and regulates the function of muscles and nerves.
- Copper: Copper is essential for the proper functioning of organs and metabolic processes.
VITAMINS
Spirulina supplies several of the vitamins that all living beings need to carry on metabolic processes:
- Pyridoxine or B6: It is involved in breakdown and assimilation of protein. Protects cardiac health, reduces edema and stabilizes female hormone levels. Studies have demonstrated that B6, together with the mineral zinc, can cure some forms of schizophrenia.
- Cobalamin or B12: Vitamin B12 is essential for proper nervous system function, homocysteine metabolism, and DNA synthesis, especially in erythrocytes. Vitamin B12 is synthesized only by microorganisms and therefore is more abundant in animal foods than in plant foods. Supplementation of a minimum of 6 µg/d of vitamin B12 is essential for vegans. Spirulina is extremely rich in this rare vitamin, containing 250 percent more than beef liver, previously thought to be nature's richest source. A single serving of Spirulina easily exceeds the Recommended Daily Allowance of 1.5 to 3 mcg daily.
- Biotin: It is an enzyme that carries CO, during certain biochemical reactions involved in carbohydrate metabolism. Also acts as a co-enzyme in the assimilation of other B-complex vitamins. Biotin is destroyed by eating raw egg whites and some kinds of raw fish.
- Pantothenic acid: It is also called as the "stress" vitamin, used by the adrenal glands, along with cholesterol and vitamin C, to manufacture cortisone and other steroids in response to physical and mental stress. Its deficiency encourages sensitivity to allergy, infection and degenerative diseases such as arthritis and rheumatism. Ulcers and hypoglycemia have also been associated with shortage of this vitamin.
- Folic acid: It is essential to proper hemoglobin formation in red blood cells. Its deficiency results in anemia, poor growth, skin pigmentation disorders and premature graying of the hair.
- Niacin: It is essential for wellbeing of mental health. It has been also recognized as an effective cholesterol lowering agent.
- Riboflavin or B2: It is associated with eye vision. Its deficiency results in cataracts, failing vision, watery eyes and uncontrollable eczema.
- Thiamine or B1: A co-enzyme in the breakdown of dietary carbohydrate. It maintains levels of glucose in the blood. Its deficiency results in weakness, cardiac damage, abdominal distention and poor oxygenation. Its severe shortage can lead to even death.
- Tocopherol or vitamin E: Spirulina contains more vitamin E per gram than pure wheat germ. This nutrient protects heart and vascular health, promotes oxygenation of cells, and retards aging.
ANTIOXIDANTS
When oxygen combines with the complex metabolic molecules it creates compounds called free radicals. Small quantities of free radicals are produced during normal body metabolism, such as breathing and digestion. Large quantities are present in many of the pollutants our bodies are exposed to, like smoke, burnt food, car exhaust, and many chemicals. Free radicals are highly unstable molecules ready to react (oxidize) with anything and they can trigger a chain reaction that produces other free radicals and can cause cell damage. Damage to cells includes the DNA; and damage to the DNA of our cells is now thought to be a major component of the aging process. An antioxidant is capable of joining with a free radical and rendering it harmless. Spirulina is rich in antioxidants including:
- Carotenoids
- Phycocyanin
- Super oxide dismutase (SOD)
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin E
PHYTONUTRIENTS
Phycocyanin:The most important pigment in Spirulina, evolved a billion years before chlorophyll and may be the precursor to chlorophyll and hemoglobin. It has both magnesium and iron in its molecular formation. Phycocyanin is related to the human pigment bilirubin, which is important to healthy liver function and digestion of amino acids. It imparts its anticancer property to Spirulina.
Chlorophyll: The common feature of green foods is their high chlorophyll content. Chlorophyll is known as a cleansing and detoxifying phytonutrient. Sometimes it is called ‘green blood’ because it looks like the hemoglobin molecule in human blood. Chlorophyll has a magnesium ion at its core, giving it a green color, and hemoglobin has iron, giving it a red color. Spirulina’s beneficial effect on anemia could be due to this similarity of chlorophyll and hemoglobin and its high bioavailable iron. Spirulina has 1% chlorophyll, one of nature’s highest levels.
It increases peristaltic action and thus relieves constipation, and also normalizes the secretion of digestive acids. It soothes the inflammation and reduces the excess pepsin secretion associated with gastric ulcers. Chlorophyll appears to promote regeneration of damaged liver cells, and also increases circulation to all the organs by dilating blood vessels. In the heart, chlorophyll aids in transmission of nerve impulses that control contraction.
Another important pigment is porphyrin, a red compound that forms the active nucleus of hemoglobin. Related to this structure is the polypyrrole molecule of B12, which is essential to the formation of healthy red blood cells.
Carotenoids:Some substances in plant foods are not true vitamins, but provide the precursors from which the body can then synthesize the appropriate vitamins. The carotenoid compounds of Spirulina are of this nature, since they are used to produce vitamin A. Spirulina contains the yellow/orange pigments cryptoxanthine and beta-carotene from which vitamin A can be made. Spirulina contains carotenoids in these forms:
- Alpha-carotene
- Beta-carotene
- Xanthophylis
- Cryptoxanthin
- Echinenone
- Zeaxanthin
- Lutein
Phycocyanin enriched Nutraculture™ Spirulina for Anemia:
Anemia is the decrease in number of red blood cells (RBCs) or less than the normal quantity of haemoglobin in the blood.
Phycocyanin enriched Nutraculture™ Spirulina contains porphyrin and bio-chelated iron which help in curing anemia. Porphyrin is a red compound that forms the active nucleus of haemoglobin. High nutrient density of Phycocyanin enriched Nutraculture™ Spirulina, especially the easily assimilated protein, folic acid, vitamin E, blood-building vitamins B12, folic acid and the amino acids, make it an ideal food source for persons suffering from anemia (Tietze, 2004). Its use is most encouraged for expecting and lactating mothers.
Reference:
- Tietze HW. (2004). Spirulina Micro food Macro Blessing, NewDelhi, B. Jain Publishers at J.J. Offset Printers.
Phycocyanin enriched Nutraculture™ Spirulina for Immunity:
The immune system is the body's defense against infectious organisms and other invaders through a series of steps called the immune response. It is mainly comprises of Innate or Nonspecific immune system and Adaptive or Specific immune system. Both aspects of the immune system have cellular and humoral components by which they carry out their protective functions. In addition, there is interplay between these two systems, i.e., cells or components of the innate immune system influence the adaptive immune system and vice versa.
Cells of the innate immune system include phagocytic cells, NK cells, basophils, mast cells, eosinophiles and platelets. Cells that make up the adaptive immune system include the B and T lymphocytes. A specialized subset of cells called antigen presenting cells (APCs) are a heterogenous population of leukocytes that play an important role in innate immunity and also act as a link to the adaptive immune system by participating in the activation of helper T cells (Th cells). These cells include dendritic cells and macrophages (Male et al., 2006).
Phycocyanin enriched Nutraculture™ Spirulina is having immune- stimulating and antiviral activities. It acts directly on myeloid lineages and either directly or indirectly on Lymphocytes, Macrophages, Hematopoetic stem cells and NK cells (Blinkova et. al., 2001; Hirasahi et. al., 2002). It also stimulates the production of Interferon gamma (IFN-γ) and other cytokines (Yakoot et. al., 2012; Hirasahi et. al., 2002). It contains bioactive proteins to stimulate the intestinal immune system and enhance the responsiveness to vaccines (Selmi et. al., 2011).
References:
- Male D, Brostoff J, Roth DB, Roitt I. (2006). Immunology- Seventh Edition, Canada, Mosby Elsevier.
- Blinkova LP, Gorobets OB, Baturo AP. (2001). Biological activity of Spirulina. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 2:114-8.
- Hirahashi T, Matsumoto M, Hazeki K, Saeki Y, Ui Mc, Seya T. (2002). Activation of the human innate immune system by Spirulina: Augmentation of interferon production and NK cytotoxicity by oral administration of hot water extract of Spirulina platensis. International Immunopharmacology. 2: 423– 434.
- Yakoot M, Salem A. (2012). Spirulina platensis versus silymarin in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus infection. A pilot randomized, comparative clinical trial. BMC Gastroenterology. 12:32-40.
- Selmi C, Leung PSC, Fischer L, German B, Yang CY, Kenny TP, Cysewski GR, Gershwin ME. (2010). The effects of Spirulina on anemia and immune function in senior citizens. Cellular & Molecular Immunology. 2011: 1–7.
Phycocyanin enriched Nutraculture™ Spirulina for Diabetes:
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder due to:
- Insufficient production of Insulin.
- Production of defective Insulin.
- Inability of cells to use insulin properly and efficiently. Insulin is a peptide hormone produced by β cells of Pancreas. It aids in:
- Entrance of glucose in cells.
- Regulation of glucose level in blood.
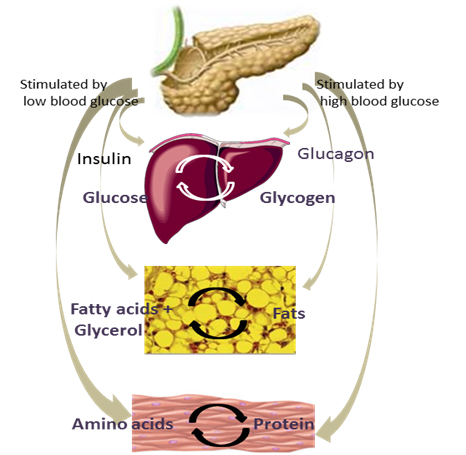
Phycocyanin enriched Nutraculture™ Spirulina has shown to perform regulatory role on lipid and carbohydrate metabolism by exhibiting glucose and lipid profile correcting activity in experimental animals and in diabetic patients (Khan et al., 2005).
It helps in regulation of blood glucose level in following ways:
- Utilization of glucose at peripheral sites.
- Greater uptake of glucose from blood by liver cells (Layam and Reddy et. al., 2007).
- Potentiation of the pancreatic secretion of insulin from islet β-cell (Kumari et. al., 2013).
- Stimulate glycogenesis in the liver which is enhanced by feeding (Fayzunnessa et. al., 2011)
- Inhibition of endogenous synthesis of lipids & down regulation of lipogenesis.
- Lower risk of the tissues for oxidation stress and high resistance for diabetes (Layam and Reddy et. al., 2007).
References:
- Khan Z, Bhadouria P, Bisen PS. (2005). Nutritional and Therapeutic potential of SPirulina. Current Pharmaceutical Biotechnology. 6: 373-379.
- Layam A, Reddy CLK. (2007). Antidiabetic property Of Spirulina. Diabetologia Croatica.35 (2): 29-33.
- Kumari DJ, Babitha B, Jaffar SK, Prasad MG, Ibrahim MD, Ahmed Khan MS. (2011). Potential Health Benefits of Spirulina platensis. An International Journal of Advances in Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2 (5 – 6 ): 417-422.
- Fayzunnessa N, Morshed NA, Uddin A, Parvin A, Saifur R. (2011). In vivo study on the efficacy of hypoglycemic activity of Spirulina plantesis in long evan rats. International Journal of Biomolecules and Biomedicine. 1(1): 27-33.
Phycocyanin enriched Nutraculture™ Spirulina for High Blood Pressure:
Hypertension or high blood pressure is a medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is elevated, due to which heart has to work harder than normal to circulate blood through the blood vessels.
Phycocyanin enriched Nutraculture™ Spirulina can stimulate the immunological system and the gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) present in it stimulates the prostaglandin synthesis, which are involved in regulation of the blood pressure (Lemes et. al., 2012). As it has a rich profile of antioxidants like vitamins C and E, it is further helpful in lowering of blood pressure (Kumari et. al., 2011). Spirulina is rich in potassium thus also prevents blood clots in arteries by preventing platelets aggregation.
References:
- Lemes AC, Takeuchi KP, Carvalho JCM, Danesi EDG. (2012). Fresh Pasta Production Enriched with Spirulina platensis Biomass. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol.55 (5): 741-750.
- Kumari DJ, Babitha B, Jaffar SK, Prasad MG, Ibrahim MD, Ahmed Khan MS. (2011). Potential Health Benefits of Spirulina platensis. An International Journal of Advances in Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2 (5–6 ): 417-422.
Phycocyanin enriched Nutraculture™ Spirulina for Cholesterol:
Cholesterol is a waxy steroid and is transported in the blood plasma. It is carried in the blood by molecules called lipoproteins mainly high density lipoproteins (HDL), low density lipoproteins (LDL) and very low density lipoproteins (VLDL). High cholesterol levels in blood can cause atherosclerosis, angina and other cardiovascular conditions.
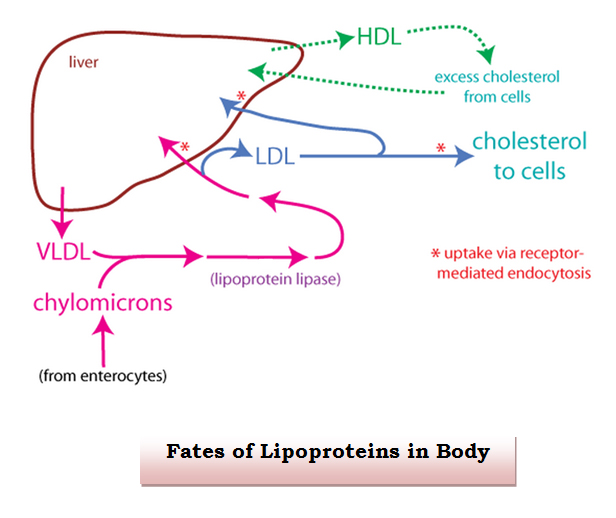
Our Phycocyanin enriched Spirulina helps in reducing blood cholesterol level particularly LDL type and thus reducing the risk of cardiovascular problems. It upregulates the HDL cholesterol, which is helpful in reverse translocation of cholesterol from blood to liver (Ramamoorthy and Premakumari, 1996). Further supplementation of Phycocyanin enriched Nutraculture™ Spirulina in your diet helps in reduction of hyper-cholesterolemic atherosclerosis (Cheong et. al., 2010). It improves general health, relieves fatigue, strengthens the spleen, regulates the blood fat level, reducs tri-glycerides, and keeps the heart healthy.
References:
- Ramamoorthy A, Premakumari S. (1996). Effect of Supplementation of Spirulina on Hypercholesterolemic Patients. J. Food Sci. Technol. 33(2): 124-128.
- Cheong SH, Kim MY, Sok DE, Hwang SY, Kim JH, Kim HR, Lee JH, Kim YB, Kim MR. (2010). Spirulina prevents atherosclerosis by reducing hypercholesterolemia in rabbits fed a high cholesterol diet. Journal of Nutritional science and vitaminology. 56(1): 34-40.
Phycocyanin enriched Nutraculture™ Spirulina for Anti-Aging:
Aging is the result of gradual decline in cellular repair and housekeeping mechanisms, which leads to an accumulation of damaged cellular constituents and ultimately to the degeneration of tissues and organs (Gelino and Henson, 2012). Possible causes of aging can be those that are built into the body system as specific DNA or RNA coding or those that are the result of controllable or uncontrollable environmental factors including radiation, nutrition, and lifestyle.
In recent years the role played by mitochondria in cellular aging has become the focus of intensive research. Oxidative damage to mitochondrial proteins might cause less efficient processing of oxygen, release of higher levels of reactive oxygen species, free radicals and increased levels of background DNA damage. Since the mitochondria are the site of production of reactive oxygen species, and so might lead to a significant overestimation of nuclear DNA damage.
Antioxidants like Vitamin E, SOD, Phycocyanin and β-carotene have potent antioxidant activity to scavenge free radicals, including alkoxyl, hydroxyl and peroxyl radicals (Deng and Chow, 2010). Phycocyanin enriched Nutraculture™ Spirulina is rich in GLA, which protects the skin from UV rays of sun. β-carotene gives elasticity to skin and together with Vitamin E, selenium and Zinc, it helps to deep cleanse the skin. Spirulina is rich in vitamins and ideal for skin treatment. Vitamin E promotes the formation of skin cells and improves blood circulation in body (Moorhead et. al., 1993).
References:
- Gelino S, Hansen M. (2012). Autophagy - An Emerging Anti-Aging Mechanism. Journal of Clinical & Experimental Pathology.; 84, 1-12.
- Deng R, Chow TJ. (2010). Hypolipidemic, Antioxidant, and Antiinflammatory Activities of Microalgae Spirulina. Cardiovascular Therapeutics.; 28(4), e33–e45.
- Kelly Moorhead K, Capelli B, Cysewski GR. (1993). SPIRULINA Nature’s Superfood, Hawaii, Cyanotech Corporation.
Phycocyanin enriched Nutraculture™ Spirulina for Allergy, Asthma & Inflammation:
Allergy is hypersensitivity towards some food material, dust, pollens or any insect bite etc. Phycocyanin enriched Nutraculture™ Spirulina is effective against various allergic responses particularly by inhibiting the release of histamine from mast cells in case of mast cell-mediated immediate-type allergic reactions (Kim et. al., 1998). Spirulina inhibits anaphylactic reactions (Yang et. al., 1997), help in curing atopic dermatitis (Nuhu et. al., 2013) and provide protection against allergic rhinitis (Cingi et. al., 2008).
Asthma is a common chronic inflammatory disease of the airways characterized by variable and chronic symptoms, reversible hinderance in airflow, and bronchospasm. Its common symptoms include shortness of breath, coughing, chest tightness and wheezing.
Phycocyanin enriched Nutraculture™ Spirulina which is a rich source of GLA, decreases the proinflammatory Prostaglandins-E2 production, which in turn led to decrease of IgE production and inflammations of air passageways. Further β-carotene, Vitamin E and Selenium content of Spirulina help in scavenging endogenous and/or environmental oxidant sources of free radicals thus help pulmonary functions to act properly (Gershwin and Belay, 2008). Rich protein content of Spirulina helps in over all maintenance of body and immune system (Labhe et. al., 2001).
Inflammation is characterized by pain, redness, swelling and heat. These symptoms result from the activities of cytokines, chemokines, histamines, leukotrienes, prostaglandins, reactive oxygen species and nitrogen species. They mainly target local blood vessels, where they enhance blood flow, induce vasodilation and increase the permeability of vessel walls (Tietze, 2004).
The role of Phycocyanin in COX-2 inhibition results in the potential application of Spirulina in the management of inflammatory conditions and toxicity due to chemicals and drugs (Belay, 2002). Spirulina has a rich profile of antioxidants which can scavenge peroxyl, hydroxyl, alkoxyl, superoxide radicals due to ROS generation. Spirulina is the potent inhibitor of NADPH oxidase which Promotes NF-kB and proliferation of cells, which further causes inflammation and inhibit neutrophil activation.
References:
- Kim HM, Lee EH, Cho HH, Moon YH. (1998). Inhibitory effect of mast cell-mediated immediate-type allergic reactions in rats by Spirulina. Biochem Pharmacol. 55(7):1071-6.
- Yang HN, Lee EH, Kim HM. (1997). Spirulina platensis inhibits anaphylactic reaction. Life Sci. 61(13):1237-44.
- Nuhu AA. (2013). Spirulina (Arthrospira): An Important Source of Nutritional and Medicinal Compounds. Journal of Marine Biology 2013: 1-8.
- Cingi C, Conk-Dalay M, Cakli H, Bal C. (2008). The effects of spirulina on allergic rhinitis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 265(10): 1219-23.
- Gershwin ME, Belay A. (2004). Spirulina in Human Nutrition and Health, Boca Raton, CRC Press.
- Labhe RU, Mani UV, Iyer UM, Mishra M, Jani K, Bhattacharya A. (2001). The effect of Spirulina in the treatment of bronchial asthma. J. Nutr. Funct. Med. Foods. 3: 53-59.
- Tietze HW. (2004). Spirulina Micro food Macro Blessing, NewDelhi, B. Jain Publishers at J.J. Offset Printers.
Phycocyanin enriched Nutraculture™ Spirulina for Anti-Cancer:
Cancer is characterized by uncontrolled proliferation of cells. Usually the timing and extent of cell division is under strict control of network of signals. Mutation in any of the node of this network can trigger cancer. Cellular biologists have defined a system of special enzymes called endonuclease which repair damaged DNA to keep cells alive and healthy. When these enzymes are deactivated by radiation or toxins, errors in DNA go unrepaired, and cancer may develop.
Several studies show that Spirulina can prevent or inhibit cancer in humans and animals. In vitro studies suggest that polysaccharides of Spirulina enhance cell nucleus enzyme activity and DNA repair synthesis (Estrada et. al., 2001).
Polysaccharides of Spirulina improve the immune system to combat against cancer-drug resistance. Spirulina induces apoptosis in tumour cells as evidented by presence of hypodiploid DNA population, caspase activation, DNA fragmentation, etc. It has also been suggested by Karkos et. al., 2011, that combined antioxidant and immune modulation characteristics of Spirulina has a possible anticancer mechanism.
References:
- Estrada JEP, Besco´ s PB, Villar del Fresno AM. (2001). Antioxidant activity of different fractions of Spirulina platensis protean extract. IL Farmaco. 56: 497–500.
- Karkos PD, Leong SC, Karkos CD, Sivaji N, Assimakopoulos DA. (2011). Spirulina in Clinical Practice: Evidence-Based Human Applications. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2011: 1-4.
Phycocyanin enriched Nutraculture™ Spirulina for Weight Management:
Phycocyanin enriched Nutraculture™ Spirulina can be used for weight loss. It is low in calories, fat, highly digestible and what is very important, it is in its natural balance (Tietze, 2004). Spirulina contains both Tyrosine and Phenylalanine, which directly influence the neurotransmitters (norepinephrine and dopamine) in brain which control appetite (Ramamoorthi and Premakumari, 1996). It is a rich source of GLA, which has a specific effect on the endocrine system, helping restore hormone, health and normalise insulin activity, so blood sugar levels stabilise and hunger cravings reduce.
References:
- Tietze HW. (2004). Spirulina Micro food Macro Blessing, NewDelhi, B. Jain Publishers at J.J. Offset Printers.
- Ramamoorthy A, Premakumari S. (1996). Effect of Supplementation of Spirulina on Hypercholesterolemic Patients. J. Food Sci. Technol. 33(2): 124-128.
Phycocyanin enriched Nutraculture™ Spirulina for Beauty:
Spirulina is very rich in β-carotene, which protects the skin by providing elasticity. Together with vitamin E, Selenium and Zinc, β-carotene helps to deep cleanse the skin. Chlorophyll in Spirulina is very beneficial for a healthy skin, due to its cell building factor and oxygen storing ability. It is also beneficial against skin inflammations. Gamma Linolenic acid (GLA) present in Spirulina protects the skin against UV radiation, dehydration and activates the blood circulation of the skin. Minerals are easily absorbed by the skin and are beneficial for an optimal function of the skin. The high content of the natural amino acid like Tyrosine in Spirulina slows down the ageing process of cells. It is also involved in the coloration of hair and skin, and helps with sun burn protection. Vitamins presence is suitable as a nourishing moisturiser for dry older skin with under active sebaceous glands. As a natural antioxidant, Vitamin E promotes the formation of skin cells, improves blood circulation and helps relieve symptoms of dermatitis and acne in teenagers (Moorhead et al., 1993; Tietze, 1999).
References:
- Kelly Moorhead K, Capelli B, Cysewski GR. (1993). SPIRULINA Nature’s Superfood, Hawaii, Cyanotech Corporation.
- Tietze HW. (1999). Spirulina Micro food Macro Blessing, NewDelhi, B. Jain Publishers at J.J. Offset Printers.
Phycocyanin enriched Nutraculture™ Spirulina for Thyroid Functioning:
Within the endocrine system, thyroid is the biological engine that ultimately directs hormonal function and, therefore, metabolism. Therefore, its proper functioning is critical to the body’s over all metabolic rate, energy (ATP) production, digestion, and many other functions. The elements most closely associated with the thyroid are iodine, tyrosine and Selenium. Thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) are consisted of a tyrosine compound (made from the amino acid phenylalanine) to which atoms of iodine are added. Selenium is the most important nutrient required for the conversion of extra T4 to T3, as T3 is a more active form. Spirulina is having natural iodine and Selenium, which nourishes the thyroid, protects all glandular tissues and ultimately supports both immune and metabolic function. Phenylalanine present in it is used by the thyroid for the production of tyrosine (Triggiani et al., 2009; Kharrazian, 2010; Shames and Shames, 2002, Tietze, 1999).
References:
- Triggiani V, Tafaro E, Giagulli VA, Sabbà C, Resta F, Licchelli B, Guastamacchia E. (2009). Role of iodine, selenium and other micronutrients in thyroid function and disorders. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 9(3):277-94.
- Kharrazian D. 2010. Why Do I Still Have Thyroid Symptoms When My Lab Tests Are Normal. Garden City, NY: Morgan James Publishing, LLC.
- Shames RL and Shames HS. 2002. Thyroid Power. New York, NY: Harper Collins Publishers Inc.
- Tietze HW. (1999). Spirulina Micro food Macro Blessing, NewDelhi, B. Jain Publishers at J.J. Offset Printers.
Phycocyanin enriched Nutraculture™ Spirulina for Fertility:
Spirulina is rich in proteins and antioxidants, which have been shown to protect the body from free radical damage, which are the causes behind fertility issues such as luteal phase defect, poor egg and sperm health, as well as lowered overall immunity and health (Kapoor and Mehta, 1993). Further, Spirulina contains only 10-15% carbohydrate content, which does not alter insulin levels and makes it safe for dibetes related infertility. Another interesting factor is that Spirulina has a relatively high content of arginine which is important for males, as the seminal fluid is 80% arginine (Tietze, 1999). Essential Fatty Acids present in Spirulina in the form of linolenic acid, linoleic acid and arachidonic acid too aid in protaglandin functions, necessary for hormonal balance and blood pressure regulation, especially important for pregnancy. Researchers also suggested that Spirulina aids in helping women with preeclampsia during pregnancy or preventing it from happening. Preeclampsia is associated with increased oxidative stress in both the placenta and vascular system of the mother. NADPH oxidase has been shown to be the number one source for oxidant stress. Phycocyanin contained in Spirulina has been shown to inhibit NADPH, which further help to protect mother and child from preeclampsia (McCarty et al).
References:
- Kapoor R, Mehta U. (1993). Effect of supplementation of blue green alga (Spirulina) on outcome of pregnancy in rats. Plant foods for human Nutrition. 43(1): 29-35.
- Spirulina for Prevention and Control of Preeclampsia, Mark F. McCarty, Jorge Barroso-Aranda, and Francisco Contreras, Oasis of Hope Hospital, Tijuana, Mexico.
- Tietze HW. (1999). Spirulina Micro food Macro Blessing, NewDelhi, B. Jain Publishers at J.J. Offset Printers.
Phycocyanin enriched Nutraculture™ Spirulina for Pregnant and Nursing Mothers:
Pregnancy is throughout a great responsibility, as a woman has to provide a constant supply of good nutrients for proper building of the child’s body tissue. So nutrition during pregnancy is especially important. Even after child is delivered, lactation imposes a greater strain on the mother; because the woman nourishes a ‘fully-developed’ and ‘rapidly growing’ baby whose food needs increases day by day. Therefore, during pregnancy it is advised to increase her protein intake from 54 to 74 grams while increase in calories should be 340 Kcal in 2nd trimester and 452 Kcal in 3rd trimester (Brown, 2011). So additional protein must be low in calories to avoid an unnecessary weight gain. Iron deficiency anaemia is also one of the commonest problem afflicting in pregnant and nursing mothers. Further, recommended daily intake for vitamin B12 in pregnant women is 2.6 µg per day and 2.8 µg during lactation periods (Brown, 2011). Hence, the diet of a expecting & nursing mother should be rich in nutrients, which the baby is taking through the milk. Spirulina has long been used safely as a food, and even at high doses, no adverse effects or teratogenicity was observed. Hence, its consumption is safe to pregnant women.
It is recommended for pregnant and nursing mothers as they need Spirulina’s extra easy-to-digest complete protein and bioavailable iron. National Institute of Nutrition (NIN), Hyderabad has conducted several studies for Spirulina effect against anaemia and reports suggested that intake of Spirulina can plug iron deficiency among anaemic pregnant women. Moreover Spirulina is the only available plant source of vitamin-B12 and rich source of GLA the main precursor to the body’s prostaglandins, the chemical which control many of body functions (Umesh, 2002).
Preeclampsia, characterized by high blood pressure, water retention and increased amount of protein in urine is very common during 2nd and 3rd trimesters of pregnancy and even just after delivery. If left untreated it can lead to premature delivery, termination of delivery or stop the child growth. Sufficiently high intake of Spirulina may have potential for prevention and control of preeclampsia. Possible mechanism must be presence of high-dose folate supplementation in Spirulina, which acts as a scavenger of peroxynitrite, one of the major cause of Preeclampsia (Rezk et al., 2003).
References:
- Brown LS. (2011). Nutrition requirements during pregnancy In Sharlin J, Edelstein S (Ed.), Essentials of Life, USA, Jones and Barlett Publishers, pp. 1-20.
- B.V.Umesh. (2002). Discover the amazing power of Spirulina Unicorn Books publishes, new Delhi, pp-19.
- Rezk BM, Haenen GR, van der Vijgh WJ, Bast A. (2003). Tetrahydrofolate and 5-methyltetrahydrofolate are folates with high antioxidant activity. Identification of the antioxidant pharmacophore. FEBS Lett. 555(3):601-5.
Who Should Consume NutraCulture™ Spirulina?
Spirulina has no reported side effects and can be consumed by everybody for the improvement of their general health. However it is especially beneficial for:
- Those on restricted diet.
- Pregnant women and nursing mothers.
- Those living a stressful, active and modern lifestyle.
- Those consuming fewer than three balanced meals a day.
- Who are regularly subjected to intense physical activity.
- Who do not get the recommended intake of fresh fruits & vegetables.
Best Value for Money
- Intake of Phycocyanin enriched “NutraCulture™ Spirulina” provides all essential ingredients like β-carotene, Iron, GLA, Amino Acids, Chlorophyll and Superoxide Dismutase, which no single fruit or vegetable can provide, when consumed in comparable amounts.
- It provides you and your family a complete nutritional-cum-antioxidant support and guards them against viral, bacterial, fungal and other infections by enhancing the immunity.
Recommended Dosage:
An intake of 4 - 6 tablets (500 mg each) per day per adult is widely recommended.
Advisory:
Consult your family physician before taking any food or dietary supplement.
